We know that smoking can wreak havoc on a woman's appearance, (as explained in previous articles on this blog) causing a sallow complexion and premature ageing, and as well as having effects on sexual health contributing to infertility, early menopause, can contribute to osteoporosis.
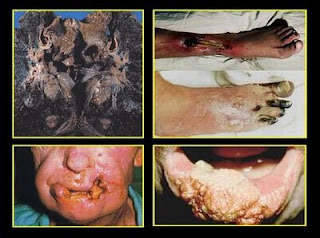 |
| Smokers lungs, mouth and skin cancers, circulatory disease leading to gangerine |
It is the adverse nicotine effect in tobacco products that leads to addiction and this which sustains tobacco use. Because most smokers are nicotine-dependent, they continue to expose themselves to toxins from cigarettes. It is the other chemicals in cigarettes, not nicotine, which are responsible for most of the adverse health effects related to smoking. Nicotine is an addictive drug. When smoked, it is delivered into the lungs and is rapidly absorbed by the blood, reaching the brain within approximately ten seconds. At this point, smokers experience a nicotine "hit" - causing the brain to produce Dopamines, a neurotransmitter that regulates emotion and feelings of pleasure. The brain soon comes to expect regular doses of nicotine and suffers nicotine withdrawal symptoms when the supply is interrupted. The addictive nature of nicotine is largely due to its dose and rapid delivery to the brain when smoking cigarettes.
Women who carry on smoking in pregnancy endanger not only themselves, but their babies too. Mothers who smoke around their children also put their kids' health at risk. Even before conceiving research shows that cigarette smoking is harmful to a woman's ovaries. It can cause a woman's eggs to be more prone to genetic abnormality and increase the risk of spontaneous miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy. Women who smoke take longer to conceive with the chances of conceiving falling by up to 40 per cent per menstrual cycle. The more cigarettes you smoke the longer it takes to become pregnant. Just one cigarette a day can have a significant impact. In men stopping smoking can reduce the risk of erectile dysfunction and may improve sexual potency.
RISKS YOU CAN LESSEN IF YOU QUIT SMOKING
• Harming ovaries
• genetic abnormalities
• miscarriages
• ectopic pregnancy
• IVF attempts improve increasing the success of fertility treatment.
There is a reduction in the likelihood of the embryo implanting compared to non-smokers, and nearly twice as many IVF attempts may be required to conceive in smokers. Breathing in secondary smoke can cause nearly as much harm as a woman smoking herself.
Like every mum-to-be you want to have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby. The best way to ensure this is not to smoke and avoid all smoking dangers. Smoking during pregnancy harms you and it harms your baby.
THE SMOKING DANGERS YOU CAN AVOID IF YOU QUIT SMOKING
- Poisonous chemicals in cigarette smoke passing through your body into your baby.
- Cigarette smoke disrupting the flow of blood to your baby.
- Prenatal passive smoking influences placental and fetal development, reduces birth weight, and affects lung and brain development.
- A smaller, weaker baby that will be more prone to infections and illness.An increased risk of breathlessness and wheezing in young babies.
- Increased risk of congenital defects such as cleft lip and/or palate or limb deformities.
Stopping smoking at any stage of pregnancy is very beneficial. The moment you quit you start increasing your chances of a healthier pregnancy and a healthier baby. You will have more energy, be able to cope better with pregnancy, and know you are doing the best for your unborn baby. Passive smoking is equally dangerous for your unborn baby. If your family or friends smoke near you, you will breathe in harmful gases and chemicals and pass them onto your baby. Passive smoking becomes more harmful for mothers who exceeds the age of 30. There is more of a risk of sudden death symptoms for new born babies if their parents were smokers. Passive smoking also increases the possibility of having respiratory diseases for children before the school age; it also increases the possibility of having heart diseases that reaches the rate of 50%, hence, increase the risk of Angina due to the increase damage of the cells in the heart muscle because of carbon monoxide and nicotine. Studies have shown that certain parts of the chromosomes were more affected by the tobacco, which lead to blood cancer (leukaemia). This may explains the relationship between smoking during pregnancy and leukaemia in children. Children growing up in a smoke free home are less likely to catch colds, coughs and bugs. And you will reduce the risk of serious problems like cot death, asthma, chest infections, and glue ear and you and your partner will feel healthier, should have fewer coughs and colds, and have more energy to run around and play with your children.
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN YOU QUIT?
20 minutes: Your blood pressure and pulse rate return to normal
8 hours: Oxygen levels in your blood return to normal.
24 hours: Carbon monoxide has been eliminated from your body. Your lungs start to clear out mucus and other smoking debris.
48 hours: There is no nicotine left in your body. Your ability to taste and smell is greatly improved.
72 hours: Breathing becomes easier. Your bronchial tubes begin to relax and your energy levels increase.
2-12 weeks: Circulation improves throughout the body, making walking and running a whole lot easier.
3-9 months: Coughs, wheezing and breathing problems get better as your lung function is increased by up to 10%.
5 years: Heart attack falls to about half that of a smoker.
10 years: Risk of lung cancer falls to half that of a smoker. Risk of heart attack falls to same as someone who has never smoked.




